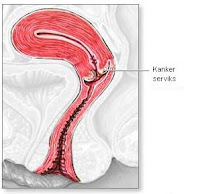
Treatment of precancerous lesions
Treatment of precancerous lesions of the cervix depends on several factors:
- The level of lesion (whether low or high level)
- Plan to become pregnant again with
- Age and general condition of the patient.
Low-level lesions usually do not require further treatment, especially if an abnormal area has been entirely removed at the time of biopsy. But the patient should undergo Pap smears and pelvic examinations regularly.
Treatment of precancerous lesions can be:
Cryosurgery (freezing)
Cautery (burning, also called diathermy)
Laser surgery to destroy the abnormal cells without harming surrounding healthy tissue
LEEP (loop electrosurgical excision procedure) or konisasi.
After treatment, patients may feel cramping or other pain, bleeding or watery discharge from the vagina. In some cases, may need a hysterectomy (removal of uterus), particularly if abnormal cells are found in the cervical opening. Hysterectomies performed if the patient does not have a plan to become pregnant again.
Treatment for cervical cancer
Selection of treatment for cervical cancer depends on the location and tumor size, stage of disease, age, general state of the patient and the patient plans to become pregnant again.
Surgery
In carcinoma in situ (cancer confined to the outermost layer of the cervix), the cancer often can be removed with the aid of a scalpel or by LEEP. With such treatment, patients can still have children. Because cancer can recur, it is recommended to undergo re-examination and Pap smear every 3 months for a first year and thereafter every 6 months. If the patient does not have a plan to get pregnant again, it is recommended to undergo a hysterectomy.
In invasive cancer, a hysterectomy and removal of surrounding structures (the procedure is called a radical hysterectomy) and lymph nodes. In young women, the ovaries (ovarian) are still functioning normally and is not removed.
Radiation therapy
Radiation therapy (radiotherapy) is effective for treating invasive cancer is still confined to the pelvic area. In radiotherapy used high-energy rays to damage cancer cells and stop its growth.
There are 2 types of radiotherapy:
- External radiation: berasar rays from a large machine
Patients do not need hospitalization, radiation is usually done as much as 5 days / week for 5-6 weeks.
- Internal radiation: radioactive substances contained in a capsule is inserted directly into the cervix.
This capsule is left for 1-3 days during which patients were treated in hospital. This treatment can be repeated several times for 1-2 weeks.
Side effects from radiation therapy are:
- Irritation of the rectum and vagina
- Damage to the bladder and rectum
- Ovaries stop functioning.
Chemotherapy
If the cancer has spread beyond the pelvis, sometimes advised to undergo chemotherapy. In the chemotherapy drugs used to kill cancer cells. Anti-cancer drugs can be administered via intravenous injection or by mouth. Chemotherapy is given in a cycle, it means a period of treatment interspersed with periods of recovery and treatment, interspersed with recovery of premises, and so on.
Biological Therapy
In biological therapies used substances to improve the immune system to fight disease. Performed on biological therapy of cancer that has spread to other body parts. The most commonly used are interferon, which can be combined with chemotherapy.
Side effects of treatment
In addition to killing cancer cells, the treatment also causes damage to healthy cells that often cause side effects that are not menyenangkan.Efek side of pengobatankanker highly dependent on the type and extent of treatment. In addition, the reaction of each patient were also different.
Methods to remove or destroy cancer cells on the surface of the cervix together with the methods used to treat precancerous lesions. Side effects that arise in the form of cramps or other pain, bleeding or watery discharge from the vagina.
A few days after a hysterectomy, the patient may experience pain in the lower abdomen. To overcome this problem can be awarded nyeri.Penderita reliever also may experience difficulty in urination and defecation. To assist urinary drainage catheter can be installed. Moments setealh surgery, the patient should be limited to the activity of healing goes well. Normal activity (including intercourse) usually can be re-done within 4-8 weeks.
After a hysterectomy, the patient will not menstruate again. Hysterectomy usually does not affect sexual desire and ability to engage seksual.Tetapi many patients who experience emotional disturbances after hysterectomy. The view of sexuality can be changed patient and the patient felt lost because she could not get pregnant again.
During the radioterap, patients prone to fatigue, especially a week sesudahnya.Istirahat enough is important, but doctors usually recommend that people stay active as much as possible. In external radiation, hair loss often occurs in areas that are illuminated and the skin becomes red, dry and itchy. Maybe the skin will become darker.
The irradiated area should be getting enough air, but must be shielded from the sun and the patient should not wear clothing that can irritate the irradiated area.
Typically, for patients undergoing radiotherapy should not be having sex. Sometimes after internal radiation, the vagina becomes narrower and less flexible lebh, so that it can cause pain during sexual intercourse. To overcome this, patients are taught to use the dilators and lubricants with water-based materials. In radiotherapy can also arise diarrhea and frequent urination.
Side effects of chemotherapy depend on the type and dose of drug used. In addition, its side effects on each patient is different. Usually anti-cancer drugs will affect cells that divide rapidly, including blood cells (which fights infection, help blood clot, or carry oxygen throughout the body).
If blood cells are exposed to the influence of anti-cancer drugs, patients would be more prone to infection, easy bruising and bleeding as well as lack of energy. Cells in hair roots and cells that line the digestive tract also divide rapidly. If the cells affected by chemotherapy, the patient will experience hair loss, decreased appetite, nausea, vomiting or open sores in the mouth.
Biological therapies can cause flu-like symptoms, namely chills, fever, muscle pain, weakness, decreased appetite, nausea, vomiting and diarrhea. Sometimes the rash appears, other than that the patient also can easily bruising and bleeding.
PREVENTION
There are two ways to prevent cervical cancer:
Preventing HPV infection
Perform Pap smears regularly.
Pap smear (Papanicolaou test) is a microscopic examination of cells obtained from serviks.Pada smear Pap smears, cervical cell samples obtained with the aid of a spatula made of wood or plastic (which is applied to the outside of the cervix) and a small brush (which is inserted into the cervical channel).
Cervical cells are then smeared on a glass object and then given a preservative and sent to a laboratory for diperiksa.24 hours before undergoing a Pap smear, you should not do the washing or rinsing the vagina, no sexual intercourse, do not soak and do not use tampons.
Pap smears are very effective in detecting precancerous changes in serviks.Jika Pap smear results indicate cervical dysplasia or looks abnormal, colposcopy and biopsy is usually performed
Prompts for doing Pap smears on a regular basis:
Every year for women aged over 35 years
Every year for women who have multiple sexual partners or have had HPV infection or genital warts
Every year for women who use birth control pills
Every 2-3 years for women aged over 35 years if 3 times consecutive Pap smears showed negative results, or for women who have undergone hysterectomy because of cancer not
As often as possible if the Pap smear shows abnormal
As often as possible after the assessment and treatment of precancerous or cervical cancer.
To reduce the possibility of cervical cancer should be:
- Girls aged under 18 years of not having sex.
- Do not have sex with genital warts sufferers or use condoms to prevent transmission of genital warts
- Do not keep changing sexual partners
- Stop smoking.
A pelvic examination every year (including Pap smears) should be started when a woman begins having sexual intercourse active or at age 20 years. Any abnormal results should be followed by colposcopy and biopsy. Several researchers have shown that vitamin A berpertan in stopping or preventing malignant changes in cells, as occurs on the surface of the cervix.
Read our popular entries:
Breast cancer
Treatment of breast cancer
Popular Entry
- Getting rid of worms with Herbs
- Yogurt Prevent Gastritis and Stomach Ulcer
- Coffee Tribulus for Vitality and Stamina
- Minimize negative effects of smoking
- 6 Point Stimulation Shocking
- Efficacy and benefits of papaya
- Five natural ingredients that address the Fat
- Aloclair Gel, Drugs for Sprue
- Quick having Pregnant and Having Children
- Efficacy cashew