Usually treatment is started after a thorough assessment of the condition of the patient, which is about a week or more after the biopsy. Treatment consists of surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy and hormone inhibitors.
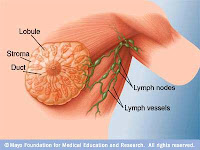
Radiation therapy is used to kill cancer cells in the removal of the tumor and the surrounding area, including the lymph nodes. Chemotherapy (a combination of drugs to kill cells that berkembanganbiak quickly or pressing breeding) and drug-hormone inhibitors (drugs that affect the hormones that promote the growth of cancer cells) are used to suppress the growth of cancer cells throughout the body.
Treatment for localized breast cancer
For cancer confined to the breast, treatment almost always involves surgery (done immediately after diagnosis) to raise as much as possible of the tumor. There are several surgical options, the main choice is mastectomy (removal of entire breast) or breast-conserving surgery (only the tumor and surrounding normal tissue).
Breast-conserving surgery
Lumpectomy: removal of the tumor and a small amount of surrounding normal tissue
Wide excision or partial mastectomy: removal of the tumor and surrounding normal tissue more
Kuadrantektomi: appointment of a quarter of the breast.
Removal of the tumor and some surrounding normal tissue provides the best chance to prevent a recurrence of cancer. The main advantages of breast-conserving surgery plus radiation therapy is cosmetic. Usually the side effects of radiation does not cause pain and lasted not long. The skin looks red or blistered.
Mastectomy
Mastectomy simplex: all breast tissue is removed but the muscles under the breast is left intact and left enough skin to cover the incision. Breast reconstruction is more easily done if the chest muscles and other tissues under the breast is left intact. This procedure is commonly used to treat invasive cancer that has spread outside the ducts, because if done breast-conserving surgery, cancer recurrence.
Simplex mastectomy plus lymph node dissection or modified radical mastectomy: all breast tissue is removed, leaving the muscles and skin, with removal of underarm lymph nodes.
Radical mastectomy: the breast, chest muscles and other tissues removed.
Radiation therapy is performed after the surgery, will greatly reduce the risk of cancer recurrence on the chest wall or in lymph nodes in the vicinity. Tumor size and the presence of tumor cells in lymph nodes affect the use of chemotherapy and hormone inhibitors. Some experts believe that the tumor diameters smaller than 1.3 cm can be treated with surgery alone. If a tumor diameter larger than 5 cm, usually given chemotherapy after surgery. If a tumor diameter greater than 7.6 cm, chemotherapy is usually given before surgery.
Patients with carcinoma in situ lobuler can remain in a strict supervision and no immediate treatment or bilateral mastectomy (removal of both breasts). Only 25% lobuler carcinomas that develop into invasive cancer that many patients who choose not to undergo treatment. If patients choose to undergo treatment, then performed a bilateral mastectomy because the cancer does not always grow at the same breast carcinoma lobuler.
If patients want treatment than mastectomy, then given the drug tamoxifen and hormone inhibitors. After undergoing a mastectomy simplex, most patients with ductal carcinoma in situ has never experienced a relapse. There are also many patients who undergo a lumpectomy, sometimes combined with radiation therapy. Inflamatoir Breast cancer is a very serious cancer, although rare. Looks like the infected breast, felt warm, red and swollen. Treatment consists of chemotherapy and radiation therapy.
Breast Reconstruction
Can be used for breast reconstruction silicone or saline implants or tissue taken from other body parts. Reconstruction can be done simultaneously with the mastectomy or can be done at a later date.
Lately the use of silicone safety has been questioned. Silicon sometimes seeps out of his pocket so that the implant becomes hard, causing pain and change shape. In addition, silicon laliran sometimes get into the blood.
Chemotherapy & Drugs Inhibiting Hormone
Chemotherapy and hormone inhibitors are often given immediately after surgery and continued for several months or years. This treatment is delaying the return of the cancer and prolong patient life expectancy. Providing some type of chemotherapy is more effective than chemotherapy alone. But without surgery or irradiation, these drugs can not cure breast cancer.
Side effects of chemotherapy can include: nausea, fatigue, vomiting, sores in the mouth that causes pain, or temporary hair loss. At this time vomiting is relatively rare because of the drug ondansetron. Without ondansetron, the patient will vomit as much as 1-6 times for 1-3 days after chemotherapy. Weight and duration of vomiting varies, depending on the type of chemotherapy used and patient. Over the past few months, sufferers also become more susceptible to infection and bleeding. But ultimately these side effects will disappear.
Tamoxifen is a hormone inhibitor that can be given as treatment continued after surgery. Tamoxifen is chemically related to esrogen and has some similar effects with hormone replacement therapy (such as reducing the risk of osteoporosis and heart disease and increased risk of uterine cancer). But Tamoxifen does not reduce hot flashes or vaginal dryness due to menopause change.
Treatment of breast cancer that has spread
Breast cancer can spread to various parts of the body. Parts of the body most frequently attacked are: the lung, liver, bones, lymph nodes, brain, and skin. Cancer appears on these body parts in time for years or even decades after the cancer is diagnosed and treated.
Breast cancer that has spread but does not show symptoms usually will not benefit from treatment. As a result treatment is often delayed until symptoms (eg pain) or cancer of began to deteriorate. If the patient felt pain, given the hormone inhibitors or chemotherapy to suppress the growth of cancer cells throughout the body. But if cancer is found only in the bone, then do radiation therapy. Radiation therapy is the most effective treatment for bone cancer and cancer that has spread to the brain.
Hormone inhibitors more often given to:
- A cancer that is supported by estrogen
- Patients who showed no signs of cancer for more than 2 years after diagnosis of
- A cancer that is not too threatening.
The drug is most effective when given to patients aged 40 years and still menstruate and produce large amounts of estrogen or to patients who experienced menopause 5 years ago.
Tamoxifen has few side effects sehngga drug of first choice. In addition, to stop the formation of estrogen can be performed surgery to remove the ovaries (ovarian) or radiation therapy to destroy the ovaries. If the cancer begins to spread again for months or years after the administration of hormone inhibitors, the use of other hormone inhibitor. Aminoglutetimid is a hormone inhibitor used to treat pain from cancer in bone. Hydrocortisone (a steroid hormone) is usually given at the same time, because it suppresses the formation of hydrocortisone aminoglutetimid naturally by the body.
The most effective chemotherapy is cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, paclitaxel, dosetaxel, vinorelbin, and mitomycin C. These medications are often used in addition to providing hormone inhibitors.
Prognosis
Clinical stage of breast cancer is the best indicator for determining the prognosis of this disease. 5-year survival rate in patients with breast cancer who have undergone appropriate treatment approaches:
- 95% for stage 0
- 88% for stage I
- 66% for stage II
- 36% for stage III
- 7% for stage IV.
PREVENTION
Many risk factors that can not be controlled. Some experts in diet and cancer experts believe that changes in diet and lifestyle in general can reduce the incidence of cancer. Attempted to perform an early diagnosis of breast cancer easier to treat and can be cured if it is still at an early stage. BSE (breast self-examination) is clinically and mammography as a screening procedure is 3 tools to detect cancer early.
Recent research has mentioned two kinds of drugs that are proven to reduce the risk of breast cancer, ie tamoxifen and raloxifene. Both are anti-estrogens in breast tissue. Tamoxifen has been widely used to prevent recurrence in patients who had undergone treatment for breast cancer. This medicine can be used in women who have a very high risk.
Preventive mastectomy is surgery to remove one or both breasts and is a choice to prevent breast cancer in women who have a very high risk (for example, one woman who had her breasts removed because of cancer, women with a family history of breast cancer and women who have p53 gene, BRCA1 atauk BRCA 2).
Read our popular entries:
Breast cancer
What is hypertension
Popular Entry
- Getting rid of worms with Herbs
- Yogurt Prevent Gastritis and Stomach Ulcer
- Coffee Tribulus for Vitality and Stamina
- Minimize negative effects of smoking
- 6 Point Stimulation Shocking
- Efficacy and benefits of papaya
- Five natural ingredients that address the Fat
- Aloclair Gel, Drugs for Sprue
- Quick having Pregnant and Having Children
- Efficacy cashew